How to operate a drone is a question many ask, opening up a world of aerial photography, videography, and exploration. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, from pre-flight checks and safety protocols to advanced flight maneuvers and legal considerations. We’ll cover essential controls, navigation techniques, and troubleshooting tips, ensuring you gain the confidence and knowledge for responsible drone operation.
Whether you’re a beginner eager to capture stunning aerial footage or an experienced pilot looking to refine your skills, this guide will equip you with the practical knowledge and best practices needed for a safe and enjoyable drone flying experience. We’ll delve into the intricacies of drone technology, flight planning, and legal compliance, providing a well-rounded understanding of this increasingly popular technology.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a good grasp of the regulations and safety procedures. For a comprehensive guide on all aspects, including practical advice and troubleshooting, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. This will ensure you’re well-prepared before your next flight, leading to a safer and more enjoyable drone experience.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for safe and responsible drone operation. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, damage to property, and legal repercussions. This section details the necessary steps and safety regulations.
Pre-Flight Inspection
Before each flight, perform a comprehensive inspection. This includes checking the battery level (ensuring sufficient charge for the planned flight duration), visually inspecting the propellers for damage or wear, and verifying a strong GPS signal for accurate positioning and stability. Confirm all components are securely attached and functioning correctly.
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Adhering to safety regulations and best practices is paramount. The following table summarizes key aspects of responsible drone operation.
| Regulation | Description | Importance | Consequences of Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Altitude | Respect altitude restrictions imposed by local regulations. | Ensures safety of airspace and avoids collisions with aircraft. | Fines, license suspension, legal action. |
| Visual Line of Sight | Maintain visual contact with your drone at all times. | Allows for immediate reaction to unexpected events. | Loss of control, accidents, potential legal issues. |
| No-Fly Zones | Avoid flying near airports, emergency services, and other restricted areas. | Protects critical infrastructure and public safety. | Arrest, fines, drone confiscation. |
| Privacy Concerns | Respect the privacy of others and avoid filming without consent. | Protects individual rights and avoids legal issues. | Legal action, reputational damage. |
Pre-Flight Sequence Flowchart
A clear pre-flight sequence ensures all necessary checks are completed. The following illustrates a typical flow:
[Imagine a flowchart here: Start -> Battery Check -> Propeller Inspection -> GPS Signal Check -> Component Check -> Safety Check (Regulations Review) -> Flight Plan Review -> Proceed to Takeoff or Abort]
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding your drone’s controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section covers basic controls, flight modes, and user interface differences across various models.
Basic Drone Controls

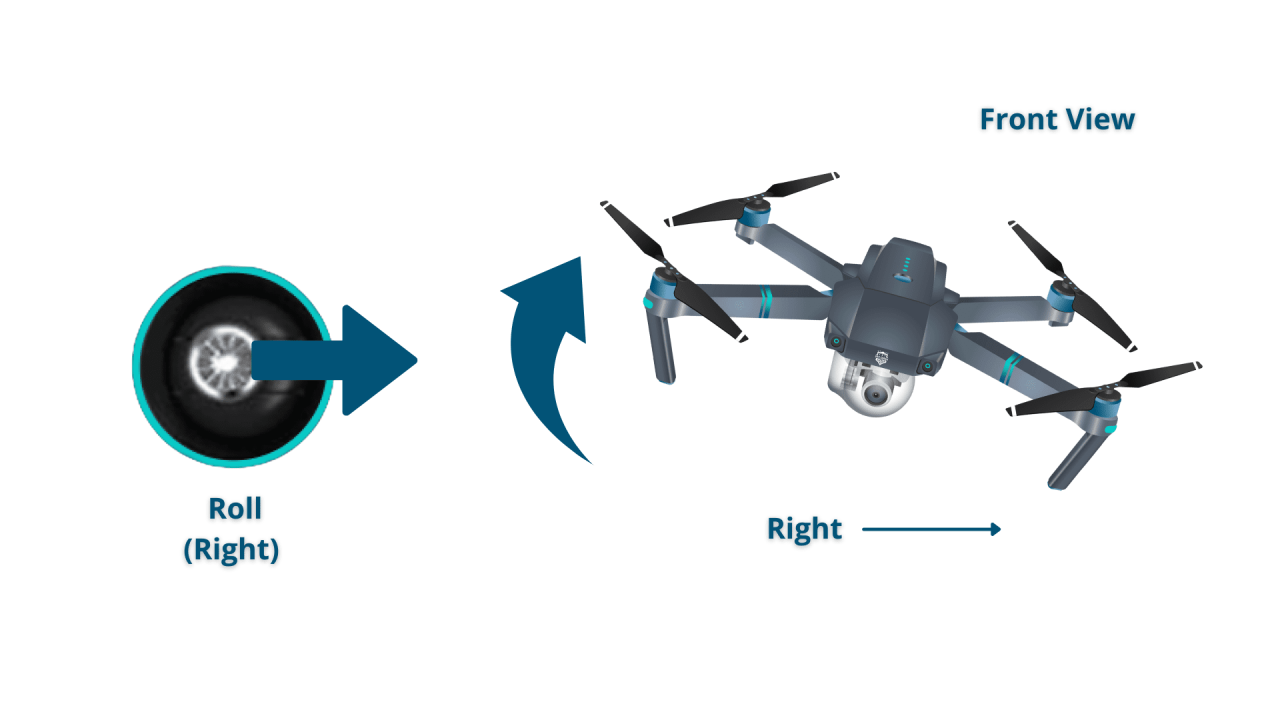
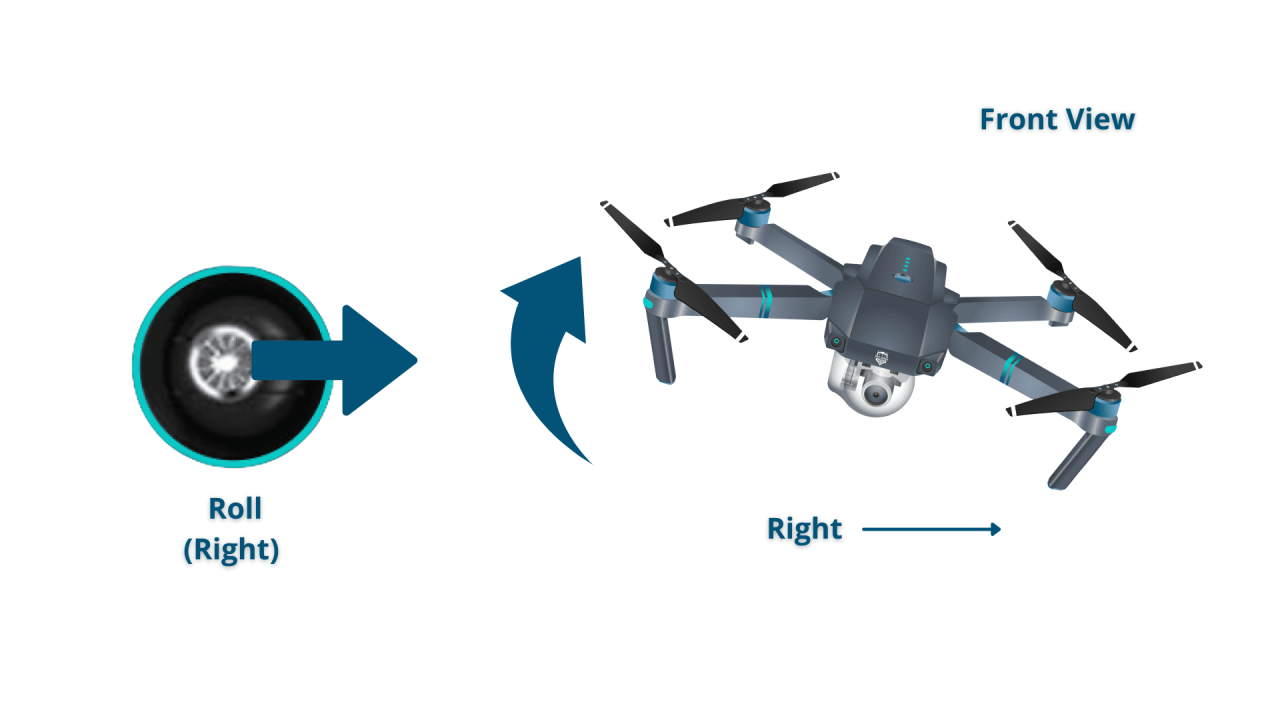
Most drones use two joysticks for primary control. One joystick typically controls yaw (rotation) and throttle (altitude), while the other controls pitch (forward/backward movement) and roll (left/right movement). Buttons on the controller often manage camera functions, flight modes, and return-to-home functionality.
Altitude Hold and GPS Positioning
Altitude hold maintains a consistent altitude, simplifying flight and reducing the risk of collisions. GPS positioning allows for precise location tracking, enabling features like return-to-home and geofencing (setting virtual boundaries for the drone).
Flight Modes
Different flight modes cater to various skill levels and flight scenarios. Beginner mode often restricts speed and maneuverability, while Sport mode allows for faster and more aggressive flying. Manual mode offers complete control, but requires significant experience and skill.
User Interface Comparison
Drone user interfaces vary across models. Key differences often include the level of customization, the availability of advanced features, and the overall ease of use.
- Model A: Intuitive interface, simple controls, limited customization options.
- Model B: Advanced features, customizable settings, steeper learning curve.
- Model C: User-friendly app, detailed flight data, integrated flight planning tools.
Taking Off, Flying, and Landing
Safe takeoff, flight, and landing procedures are essential for preventing accidents and damage. This section details the steps involved in each phase of a drone flight.
Safe Takeoff Procedure
Before takeoff, ensure the drone is in an open area, away from obstacles and people. Calibrate the compass and GPS, then gently lift off using the throttle stick, maintaining a steady ascent.
Maneuvering the Drone
Practice smooth turns and controlled ascents and descents. Avoid abrupt movements, which can destabilize the drone. Use the joysticks with precision and gradually increase speed as you gain confidence.
Safe Landing Procedure
For landing, gradually descend using the throttle stick, maintaining a slow and controlled approach. Choose a level surface free from obstacles. Once the drone is close to the ground, gently lower it until it touches down smoothly.
Handling Unexpected Situations
Unexpected situations like low battery or signal loss require immediate action. If the battery is low, immediately initiate a return-to-home function. If signal is lost, the drone may have an autonomous return-to-home feature; otherwise, you may need to wait for signal reacquisition.
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning photos and videos. Understanding camera settings and composition techniques is crucial for achieving professional-quality results.
Camera Settings Adjustments
Adjust ISO, shutter speed, and aperture to optimize image quality based on lighting conditions. Higher ISO values are suitable for low-light situations, while lower values are preferred for bright conditions. Proper shutter speed prevents motion blur.
Learning to operate a drone involves understanding its controls and safety procedures. A crucial first step is familiarizing yourself with the basics, which you can do by checking out this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. From there, practice is key to mastering the nuances of flight, ensuring safe and effective drone operation.
Composing Shots
Consider the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional techniques to create visually appealing shots. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to add depth and interest to your footage.
Camera Angles and Their Impact

Different camera angles create distinct effects. Examples include:
- Bird’s-eye view: Provides a wide, panoramic perspective.
- Low-angle shot: Emphasizes height and scale.
- Tracking shot: Follows a subject in motion.
- Dutch angle: Creates a sense of unease or disorientation.
Capturing Time-Lapse Videos
To create a time-lapse, plan your shots carefully, selecting a stable location and setting the drone’s intervalometer to capture images at regular intervals. Use drone software to plan the flight path and automate the capture process. Post-processing software can then stitch the images together into a smooth time-lapse video.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting: How To Operate A Drone
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting skills are essential for keeping your drone in top condition and resolving common issues.
Routine Maintenance Tasks
Regularly inspect the drone for any damage, clean the propellers and camera lens, and check the battery health. Keep the drone’s firmware updated for optimal performance and bug fixes.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Common malfunctions include GPS signal loss, low battery warnings, and motor issues. These can stem from various factors, such as interference, battery degradation, and mechanical problems.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
| Problem | Possible Cause | Troubleshooting Steps | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS Signal Loss | Interference, weak signal | Relocate to an open area, restart the drone, update firmware | Fly in open areas, avoid interference sources |
| Low Battery Warning | Battery degradation, overuse | Land immediately, replace or recharge the battery | Monitor battery levels, replace aged batteries |
| Motor Issues | Mechanical damage, motor failure | Inspect motors, replace faulty components | Handle drone with care, avoid collisions |
Proper Storage and Transportation
Store the drone in a dry, cool place away from direct sunlight and moisture. Use a protective case during transportation to prevent damage.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to local regulations. This section covers legal requirements, restricted airspace, and registration procedures.
Legal Requirements for Drone Operation
Regulations vary by jurisdiction. Always check with your local aviation authority for specific rules regarding drone operation, including registration requirements, permitted flight areas, and airspace restrictions. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties.
Restricted Airspace and No-Fly Zones
Airports, military bases, and other sensitive areas are typically designated as no-fly zones. Using online resources and apps can help identify these restricted areas before flight.
Drone Registration and Permits
In many jurisdictions, drone registration is mandatory. This typically involves providing information about the drone and its operator. Certain activities may also require specific permits, such as commercial operations or flights in controlled airspace.
Resources for Up-to-Date Information, How to operate a drone
Consult your country’s civil aviation authority website for the most current regulations and information related to drone operation.
Advanced Drone Techniques
This section explores advanced flight maneuvers and applications for experienced drone pilots.
Advanced Flight Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers, such as flips and rolls, are typically available on more sophisticated drone models and require a high level of skill and practice. Always ensure a safe and open environment before attempting these maneuvers.
Drone Software for Flight Planning
Specialized software allows for detailed flight planning and route creation. This is particularly useful for complex missions, such as aerial photography or surveying. These programs often provide tools for setting waypoints, adjusting altitude, and controlling camera movements.
Waypoint Navigation
Waypoint navigation allows you to program a sequence of locations for the drone to follow autonomously. This feature is valuable for creating smooth, cinematic shots or for performing repetitive tasks like inspections.
Drone Applications
Drones are increasingly used for various applications, including aerial surveying, infrastructure inspection, search and rescue operations, and precision agriculture. These applications often require specialized equipment and training.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of safe and responsible drone piloting, from pre-flight preparations to advanced flight techniques. By adhering to safety regulations, practicing consistently, and continuously learning, you can unlock the full potential of your drone while ensuring the safety of yourself and others.
Remember, responsible drone operation is key to enjoying this exciting technology to its fullest.
FAQ Corner
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and autonomous features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with good flight time and easy-to-use controls.
How often should I charge my drone battery?
Charge your drone battery after each flight and avoid fully depleting it. Store batteries at a moderate temperature to maintain their lifespan.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
If you lose control, immediately attempt to bring the drone to a safe landing. If this is impossible, engage the return-to-home function (if available) or contact local authorities if it poses a safety risk.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by location. Check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations and procedures in your area.